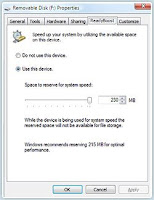
 Windows ReadyBoost improves system memory and boosts performance.Adding system memory (typically referred to as RAM) is often the best way to improve a PC's performance, since more memory means more applications are ready to run without accessing the hard drive. However, upgrading memory can be difficult and costly, and some machines have limited memory expansion capabilities, making it impossible to add RAM.Windows Vista introduces Windows ReadyBoost, a new concept in adding memory to a system. You can use non-volatile flash memory, such as that on a universal serial bus (USB) flash drive, to improve performance without having to add additional memory "under the hood."The flash memory device serves as an additional memory cache—that is, memory that the computer can access much more quickly than it can access data on the hard drive. Windows ReadyBoost relies on the intelligent memory management of Windows SuperFetch and can significantly improve system responsiveness.It's easy to use Windows ReadyBoost. When a removable memory device such as a USB flash drive or a secure digital (SD) memory card is first inserted into a port, Windows Vista checks to see if its performance is fast enough to work with Windows ReadyBoost. If so, you are asked if you want to use this device to speed up system performance. You can choose to allocate part of a USB drive's memory to speed up performance and use the remainder to store files.The capacity of the removable media must be at least 256 MBDevices larger than 4GB will have only 4GB used for ReadyBoostThe device should have an access time of 1ms or lessThe device must be capable of 2.5 MB/s read speeds for 4 kB random reads spread uniformly across the entire device and 1.75 MB/s write speeds for 512 kB random writes spread uniformly across the deviceThe device must have at least 235 MB of free spaceNTFS and FAT32 are supportedThe initial release of ReadyBoost supports only ONE device
Windows ReadyBoost improves system memory and boosts performance.Adding system memory (typically referred to as RAM) is often the best way to improve a PC's performance, since more memory means more applications are ready to run without accessing the hard drive. However, upgrading memory can be difficult and costly, and some machines have limited memory expansion capabilities, making it impossible to add RAM.Windows Vista introduces Windows ReadyBoost, a new concept in adding memory to a system. You can use non-volatile flash memory, such as that on a universal serial bus (USB) flash drive, to improve performance without having to add additional memory "under the hood."The flash memory device serves as an additional memory cache—that is, memory that the computer can access much more quickly than it can access data on the hard drive. Windows ReadyBoost relies on the intelligent memory management of Windows SuperFetch and can significantly improve system responsiveness.It's easy to use Windows ReadyBoost. When a removable memory device such as a USB flash drive or a secure digital (SD) memory card is first inserted into a port, Windows Vista checks to see if its performance is fast enough to work with Windows ReadyBoost. If so, you are asked if you want to use this device to speed up system performance. You can choose to allocate part of a USB drive's memory to speed up performance and use the remainder to store files.The capacity of the removable media must be at least 256 MBDevices larger than 4GB will have only 4GB used for ReadyBoostThe device should have an access time of 1ms or lessThe device must be capable of 2.5 MB/s read speeds for 4 kB random reads spread uniformly across the entire device and 1.75 MB/s write speeds for 512 kB random writes spread uniformly across the deviceThe device must have at least 235 MB of free spaceNTFS and FAT32 are supportedThe initial release of ReadyBoost supports only ONE device
Feb 20, 2009
Windows Vista ReadyBoost
 Windows ReadyBoost improves system memory and boosts performance.Adding system memory (typically referred to as RAM) is often the best way to improve a PC's performance, since more memory means more applications are ready to run without accessing the hard drive. However, upgrading memory can be difficult and costly, and some machines have limited memory expansion capabilities, making it impossible to add RAM.Windows Vista introduces Windows ReadyBoost, a new concept in adding memory to a system. You can use non-volatile flash memory, such as that on a universal serial bus (USB) flash drive, to improve performance without having to add additional memory "under the hood."The flash memory device serves as an additional memory cache—that is, memory that the computer can access much more quickly than it can access data on the hard drive. Windows ReadyBoost relies on the intelligent memory management of Windows SuperFetch and can significantly improve system responsiveness.It's easy to use Windows ReadyBoost. When a removable memory device such as a USB flash drive or a secure digital (SD) memory card is first inserted into a port, Windows Vista checks to see if its performance is fast enough to work with Windows ReadyBoost. If so, you are asked if you want to use this device to speed up system performance. You can choose to allocate part of a USB drive's memory to speed up performance and use the remainder to store files.The capacity of the removable media must be at least 256 MBDevices larger than 4GB will have only 4GB used for ReadyBoostThe device should have an access time of 1ms or lessThe device must be capable of 2.5 MB/s read speeds for 4 kB random reads spread uniformly across the entire device and 1.75 MB/s write speeds for 512 kB random writes spread uniformly across the deviceThe device must have at least 235 MB of free spaceNTFS and FAT32 are supportedThe initial release of ReadyBoost supports only ONE device
Windows ReadyBoost improves system memory and boosts performance.Adding system memory (typically referred to as RAM) is often the best way to improve a PC's performance, since more memory means more applications are ready to run without accessing the hard drive. However, upgrading memory can be difficult and costly, and some machines have limited memory expansion capabilities, making it impossible to add RAM.Windows Vista introduces Windows ReadyBoost, a new concept in adding memory to a system. You can use non-volatile flash memory, such as that on a universal serial bus (USB) flash drive, to improve performance without having to add additional memory "under the hood."The flash memory device serves as an additional memory cache—that is, memory that the computer can access much more quickly than it can access data on the hard drive. Windows ReadyBoost relies on the intelligent memory management of Windows SuperFetch and can significantly improve system responsiveness.It's easy to use Windows ReadyBoost. When a removable memory device such as a USB flash drive or a secure digital (SD) memory card is first inserted into a port, Windows Vista checks to see if its performance is fast enough to work with Windows ReadyBoost. If so, you are asked if you want to use this device to speed up system performance. You can choose to allocate part of a USB drive's memory to speed up performance and use the remainder to store files.The capacity of the removable media must be at least 256 MBDevices larger than 4GB will have only 4GB used for ReadyBoostThe device should have an access time of 1ms or lessThe device must be capable of 2.5 MB/s read speeds for 4 kB random reads spread uniformly across the entire device and 1.75 MB/s write speeds for 512 kB random writes spread uniformly across the deviceThe device must have at least 235 MB of free spaceNTFS and FAT32 are supportedThe initial release of ReadyBoost supports only ONE device
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
No comments:
Post a Comment